The Dangers of Sleep Deprivation to Your Brain and Body Function


Sleep deprivation is not getting the required amount of sleep for your body to function correctly. Occasional sleep issues can be annoying, but long-term lack of sleep can affect your ability to function, quality of life, and health.
The recommended amount of sleep ranges from seven to nine hours each night for adults. More sleep is required to ensure proper development and function for children and teenagers.
Your body needs sleep to function properly, just as it needs air and food. During sleep, your body heals and restores itself. Without adequate sleep, your brain and body systems won't be able to function normally.
There are short term and long term effects of sleep deprivation. Some of the effects of sleep deprivation on health, function and wellbeing include:
It doesn't take too long for some of these effects to start impacting your day to day life. The longer the sleep deprivation occurs, the worse and more long-term issues will show up.
Studies have shown that a consistent lack of sleep can dramatically lower your quality of life. It even increases the risk of early death if untreated for too long.
In most people, sleep deprivation is caused by a consistent lack of sleep or reduced quality of sleep. Getting less than seven hours of sleep on a regular basis for most adults can cause a range of issues.
Sleep deprivation can have causes that aren't due to underlying diseases such as sleep disorders. Often it's due to stress or poor sleeping habits.
In adults, so many factors could lead to sleep issues due to stressful and busy lives. However, the most common causes of sleep deprivation include:
There are lots of lifestyle and environmental factors that cause sleep deprivation, but you may have an underlying sleep disorder or another health condition. These can be harder to diagnose yourself, and it's best to chat with your doctor.
If you're struggling with poor sleep, you're likely to see noticeable signs of sleep deprivation, including:
Of course, this can look different in different people. There is also a difference in symptoms between adults and children regarding sleep deprivation.
According to the National Sleep Foundation, the target amount of sleeping hours is different depending on your age group, which are:
For most adults, a minimum of seven hours of sleep is needed to improve health and reduce fatigue symptoms. If you're unsure about your needs, you can ask your doctor or book an appointment with a sleep specialist.
The best way to prevent sleep deprivation is to ensure you get an adequate amount of sleep. Of course, this is usually easier said than done, but it's essential to try. Often, you can improve the problem by making some immediate lifestyle changes.
Suppose you're experiencing mild or occasional problems with sleep. In that case, there are some simple lifestyle changes you can try before seeing a doctor, such as:
Depending on your personal needs, you can try a whole range of other things to get back into a healthy sleep rhythm. Some more suggestions to help you get better sleep include:
There are many ways to support better quality sleep, including counselling, lifestyle changes, environmental adjustments, medication, and other alternative therapies.
If you find yourself having problems with sleep, you can talk to your doctor or find someone specialising in sleep and sleeping disorders. They can also test you for underlying health conditions that might be causing your lack of sleep.
Sometimes, sleep deprivation occurs because of more than just lifestyle factors. It can be caused by sleep disorders such as:
Sleep disorders may make it much more challenging to get a good night's sleep, even after making lifestyle changes. This is where you can seek treatment or solutions from a doctor or sleep professional.
The long term effects of sleep deprivation are real and can either lead to or be caused by other serious health conditions.
If you are living with someone suffering from a sleep disorder or other health problems as a result of sleep deprivation, you might need to administer first aid one day. You can learn how to handle these situations by doing a first aid course.
May 1, 2025
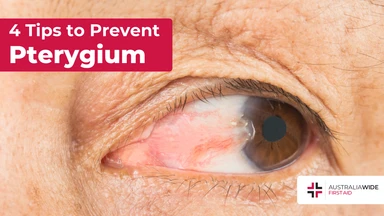
Pterygium, also known as surfer's eye, is an ocular surface disease characterised by a growth of limbal and conjunctival tissue over the cornea. Fortunately, you can practice many eye health habits to help prevent the development of pterygium and other risks.
April 3, 2025
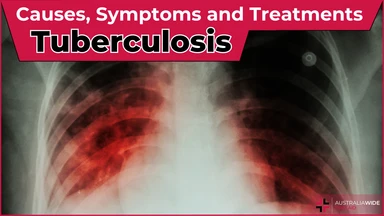
Tuberculosis is a severe bacterial infection that mainly affects the lungs and other parts of the body, including the nervous system. This contagious disease can quickly spread in crowded areas when an infected person coughs, talks, or sneezes.

February 13, 2025
Melioidosis is a bacterial infection caused by Burkholderia pseudomallei, a microorganism found in soil and water. This infection is often underdiagnosed due to symptoms mimicking many other illnesses. As such, awareness is critical for those living or working in affected regions.